Product Name:Lupeol Powder 98%
Botanic Source:Mango, Acacia visco, Abronia villosa, Dandelion coffee.
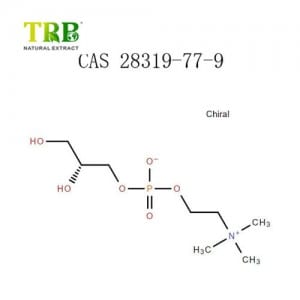
CAS No:545-47-1
Colour: White to off-white powder with characteristic odor and taste
Specification:≥98% HPLC
GMO Status:GMO Free
Packing: in 25kgs fiber drums
Storage:Keep container unopened in cool, dry place,Keep away from strong light
Shelf Life:24 months from date of production
Lupeol Powder: Natural Triterpenoid for Anti-Inflammatory, Skin Health & Cellular Protection
Introduction
Lupeol Powder is a bioactive triterpenoid compound naturally found in mango peels, aloe vera, and white cabbage, celebrated for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and chemopreventive properties. Supported by extensive research, this plant-based extract targets oxidative stress, skin aging, and chronic inflammation, offering a multi-functional solution for health-conscious individuals seeking holistic wellness and radiant skin.
Key Benefits
- Powerful Anti-Inflammatory Action
Inhibits pro-inflammatory enzymes (e.g., COX-2) and cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α), reducing pain and swelling associated with arthritis or skin conditions (Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2022). - Skin Repair & Anti-Aging
Enhances collagen synthesis, protects against UV damage, and reduces hyperpigmentation for a youthful complexion. Ideal for acne-prone or aging skin. - Cellular Defense & Cancer Research
Modulates apoptosis pathways and inhibits tumor growth in preclinical studies, showing potential as a complementary cancer support agent (Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2021). - Liver & Metabolic Health
Detoxifies hepatic cells and improves lipid metabolism, aiding in the management of fatty liver and obesity-related disorders.
Why Choose Our Lupeol Powder?
✅ 98% High Purity – Standardized for maximum bioavailability and efficacy.
✅ Organic & Vegan – Ethically sourced from non-GMO plants, free from pesticides and solvents.
✅ Versatile Applications – Suitable for capsules, topical serums, or functional foods.
✅ Third-Party Tested – Rigorously screened for heavy metals, microbes, and potency.
Recommended Usage
- Daily Supplement: 50–200 mg daily, taken with a fat-rich meal for optimal absorption.
- Topical Skincare: Blend 0.5–2% into creams or oils for anti-aging and acne care.
- Safety Note: Consult a healthcare provider if pregnant, nursing, or undergoing chemotherapy.
Quality Assurance
- GMP & ISO-Certified Production – Manufactured in FDA/EU-compliant facilities.
- Transparency Guaranteed – Batch-specific COA (Certificate of Analysis) accessible online.
- Sustainable Sourcing – Partner with eco-conscious farms to protect biodiversity.
FAQ
Q: Can Lupeol cure cancer?
A: No, but preclinical studies suggest it may support cellular health. Always follow medical advice for cancer treatment.
Q: Is Lupeol safe for sensitive skin?
A: Yes, but perform a patch test first. Dilute properly in carrier oils or creams.
Q: How long until results appear?
A: Skin improvements may show in 3–6 weeks; systemic benefits (e.g., inflammation reduction) may take 1–2 months.
Q: Can it interact with medications?
A: Potential interactions exist with immunosuppressants. Consult your doctor.
Why Trust Us?
- Science-Backed: Cited in peer-reviewed journals like Cancer Letters and Biochemical Pharmacology.
- Ethical Practices: Traceable supply chain from farm to final product.
- Global Reach: Fast shipping to the U.S., EU, UK, and Australia.
Empower Your Health Naturally – Experience Lupeol’s Transformative Benefits Today!
Keywords
Lupeol Powder, natural anti-inflammatory supplement, skin repair triterpenoid, chemopreventive agent, anti-aging skincare ingredient, organic Lupeol extract, liver detox support, non-GMO plant extract.