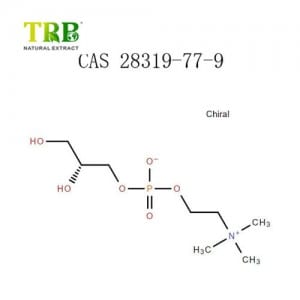
Our eternal pursuits are the attitude of “regard the market, regard the custom, regard the science” and the theory of “quality the basic, trust the first and administration the advanced” for Taxifolin Powder Larch Tree Extract, Good quality is factory’ existence , Focus on customer’ demand is the source of company survival and advancement, We adhere to honesty and superior faith working attitude, hunting forward towards your coming !
Our eternal pursuits are the attitude of “regard the market, regard the custom, regard the science” and the theory of “quality the basic, trust the first and administration the advanced” for China Taxifolin Powder and Taxifolin, Our company insists on the principle of “Quality First, Sustainable Development”, and takes “Honest Business, Mutual Benefits” as our developable goal. All members sincerely thank all old and new customers’ support. We will keep working hard and offering you the highest-quality goods and service.
| Product Name | Taxifolin Bulk Powder |
| IUPAC name | (2R,3R)-2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-2,3-dihydro-4H-chromen-4-one |
| Synonyms | Dihydroquercetin, Dihydro Quercetin, DHQ, Lavitol, Dahurian Larch extract, Larix gmelinii extract, larch tree extract, Dahurian Larch Tree Extract, taxifoline, dihydroquercétine |
| CAS Number | 24198-97-8480-18-217654-26-1 |
| Molecular Formula | C15H12O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 304.3 |
| Botanical Source | Larix sibirica |
| Specification | 98% |
| Appearance | Light yellow or off-white powder |
| Functions | Antioxidant, Vascular Protection, Anti-cancer |
Taxifolin, also called Dihydroquercetin, belongs to the flavanonol class of flavonoids, and flavanols are a class of polyphenols. It derives from quercetin powder.
Taxifolin (Dihydroquercetin) is an operative flavonoid, abundantly found in olive oil, grapes, citrus fruits, and onions.

Taxifolin vs Quercetin
Taxifolin Sources
Dahurian larch, or the Larix gmelinii, or Gmelin larch, is a larch species native to eastern Siberia and adjacent northeastern Mongolia, northeastern China (Heilongjiang), South Korea, and North Korea.
Dahurian Larch forms enormous forests in the eastern Siberian taiga, growing at 50–1,200 m altitude on boggy and well-drained soils, including on the shallow grounds above permafrost. It is the northernmost tree in the world, as creeping forms of the trees in the tundra of the Taymyr Peninsula, and as comparatively vertical growing single trees.
Dahurian larch is grown occasionally in botanical gardens in Europe and North America; it is not an easy species to grow in areas with mild winters, adapted to a long winter break.
Taxifolin Specifications
- 80% Taxifolin powder HPLC
- 90% Taxifolin powder HPLC
- 95% Taxifolin powder HPLC
- 98% Taxifolin powder HPLC
- 99% Taxifolin powder HPLC
Dihydroquercetin-glucoside (DHQG)
Dihydroquercetin-glucoside (DHQG) is a stabilized polyphenol that activates the division of hair follicle stem cells while maintaining their differentiation properties. It’s considered an excellent option for hair loss treatment.
Dihydroquercetin vs Quercetin dihydrate

Molecular Formula: C15H14O9
Molecular Weight: 338.27
Vitamin C with Dihydroquercetin
Taxifolin Manufacturing Process

Taxifolin Benefits
As an Antioxidant
A study of dihydroquercetin on the peroxidation process of liposome membranes from egg phospholipids induced by ferrous sulfate or Fe(2+)-ascorbate system showed that dihydroquercetin antioxidant activity matches the antioxidant activity of alpha-tocopherol. Therefore, it was suggested that the mechanism of the antioxidant effect of dihydroquercetin is to scavenge lipid-free radicals.
For Vascular Protection
Hyperlipidemia is the most critical factor in developing atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease due to elevated cholesterol or low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. The results showed that Taxifolin maintained average lipid profiles in rat serum and liver and lipid excretion in feces after adding cholesterol-enriched diets. The in vivo results also showed that paclitaxel-treated animals had reduced liver total cholesterol levels and reduced levels of thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances in serum and liver.
For covid-19
In recent years, the antiviral activity of Taxifolin against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which causes COVID-19, has been investigated. After extensive research, researchers found that Taxifolin may be a potential SARS-CoV-2 master protease inhibitor with the lowest predicted IC50 value among many flavonoids. In addition, Taxifolin was one of 11 potential binders identified as a significant protease inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 by another group of researchers who also performed an extensive computational screen. They also estimated low to moderate toxicity from off-target binding, improved drug similarity, and enhanced binding to the therapeutic target compared to co-crystallized ligands. These data suggest that Taxifolin is a possible anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug.
Anti-cancer
Taxifolin is a natural flavonoid that interacts with cell cycle regulators by activating the Wnt/ β -catenin signaling pathway, resulting in cell cycle arrest and tumor regression. According to several studies, Taxifolin has sound synergistic therapeutic effects in breast, lung, colorectal, liver, prostate, bone, and skin cancers.
Taxifolin side effects
Taxifolin dosage